Status of our health data
Why is our health data so valuable?
It represents a part of our personal data and is a gold mine for companies.
On medicine and research side, there is an obvious need to be able to exploit these medical data.
But what does it really contain? And why is it important for us, as patients, to understand the legislation ?

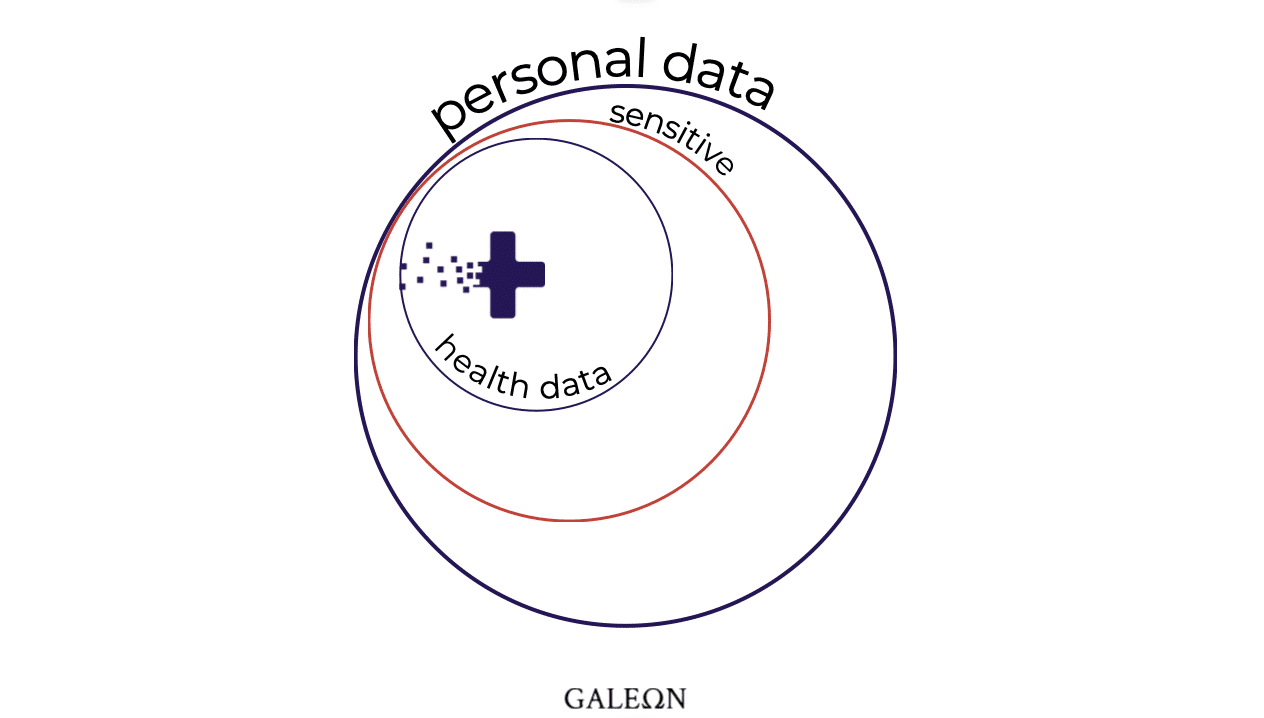
Patient data, health data..etc.
These are pretty broad terms, but do we really know what they mean?
We all know globally what a data represents. At least, in the collective consciousness.
This little piece of something, which, combined with others, allows us to understand and identify an entity. Us for example.
Some can contain sensitive information and can affect our daily actions. What is more, in terms of health.
Take for example an insurance company that would have access to your history, and suddenly decides to recalculate or increase the interest rate of your loan.
Imagine that some of your medical information is held in confidence, but that in X case, it has been disclosed? To your employer or otherwise.
In any case, it is important to understand what health data is from a legal point of view in order to ensure its protection.
? Considering the different legislations in terms of personal data, the issue is studied under the GDPR (EU side), and HIPAA/HITECH aspects (US side).

PART 1 - Definition of personnal data according to GDPR
The European Regulation for Data Protection (GDPR - Genera Data Protection Regulation), came into effect on May 25, 2018.
What does the regulation says?
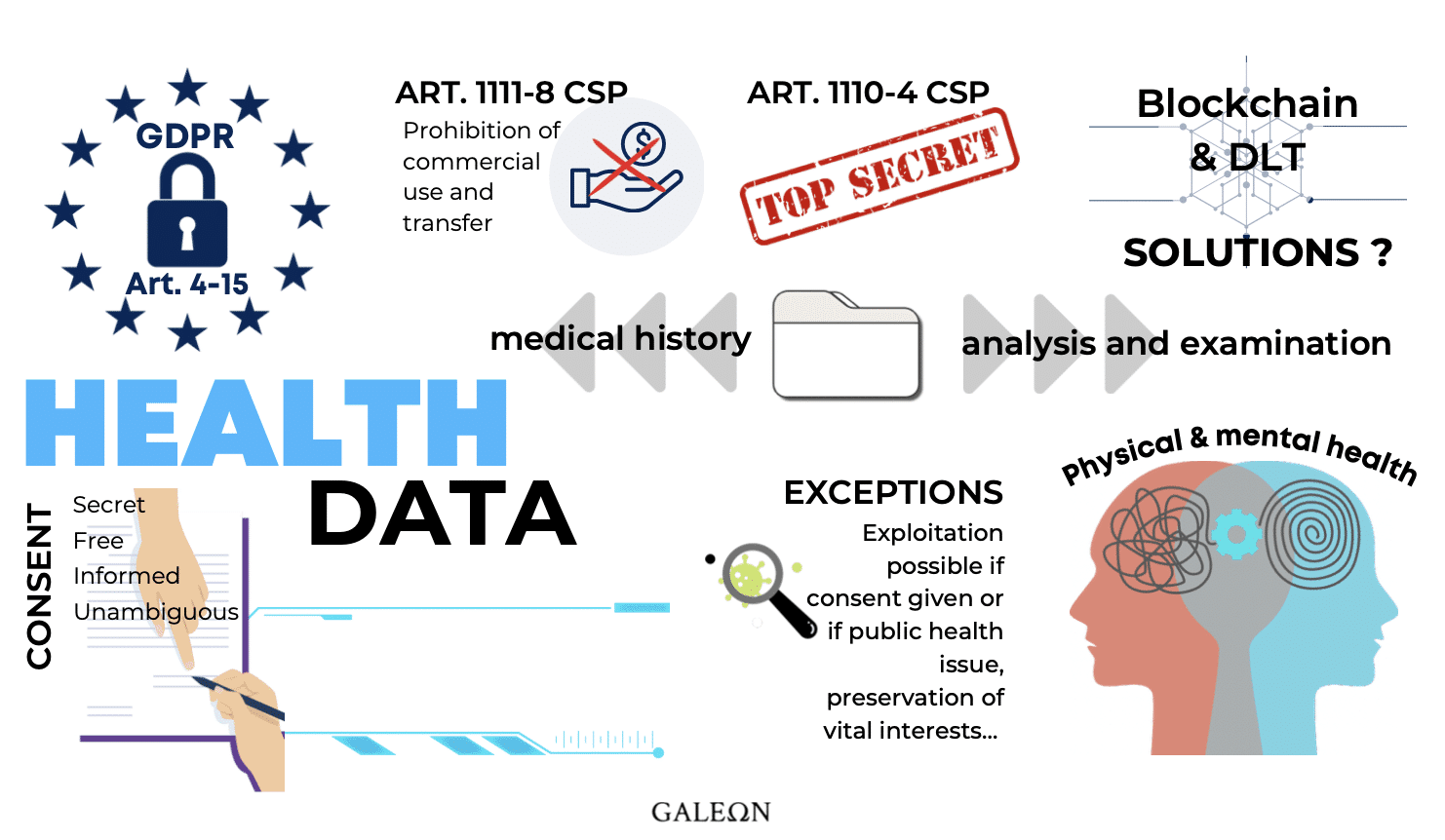
Here is the definition of health data as defined in Article 4-15 of the GDPR: it is "personal data relating to the physical or mental health of a natural person, including the provision of health care, which reveals information about the health status of that person".
Let's deconstruct this definition. First, a health data is any data that :
- relates to a natural person
- reports on mental or physical health
- and past, present or future health.
These three conditions seem to be at least necessary.

1/ Legal definition of health data (GDPR)
- Health data must be linked to a physical person.
This justification is related, for example, through the contribution of a social security identification number, or other administrative characteristics (PHI in US). In short, any element allowing to identify the person at the time of his care and throughout his follow-up.
- The temporality of the information (past/present/future) also counts, i.e., the moment when it was collected.
In other words, from the moment the patient presents with medical information and/or information useful to his care, until the completion of an examination, as well as the interpretation of this data.
- Finally, this data must be related to mental or physical health.
Therefore, all information that allows us to understand the patient's condition.
A rather broad definition finally, and which includes as well medical data which refer to the history, to units of measurements taken during an examination..etc.
? Keep in mind that each situation is studied on a case by case basis.
2/ Health data in practice
What about data from IoTs (connected objects)?
It could be considered that it depends on the nature and the crossing of these data.
Let's take a few examples:
- Data reporting overweight and revealing obesity are characterized as health data.
- Information specifying the disability of a patient receiving treatment is considered health data.
- On the other hand, the fact of specifying in a certificate the ability to practice a sport does not fall into this category.
- Conversely, stating unfitness falls within the definition. ☝️
Why is it so important to determine the nature of this information?
Depending on the qualification and sensitivity of this data, it will or will not be protected by a specific legal regime as well as by other regulations.
- Article L.1110-4 of the Public Health Code (CSP) relating to the provisions on secrecy.
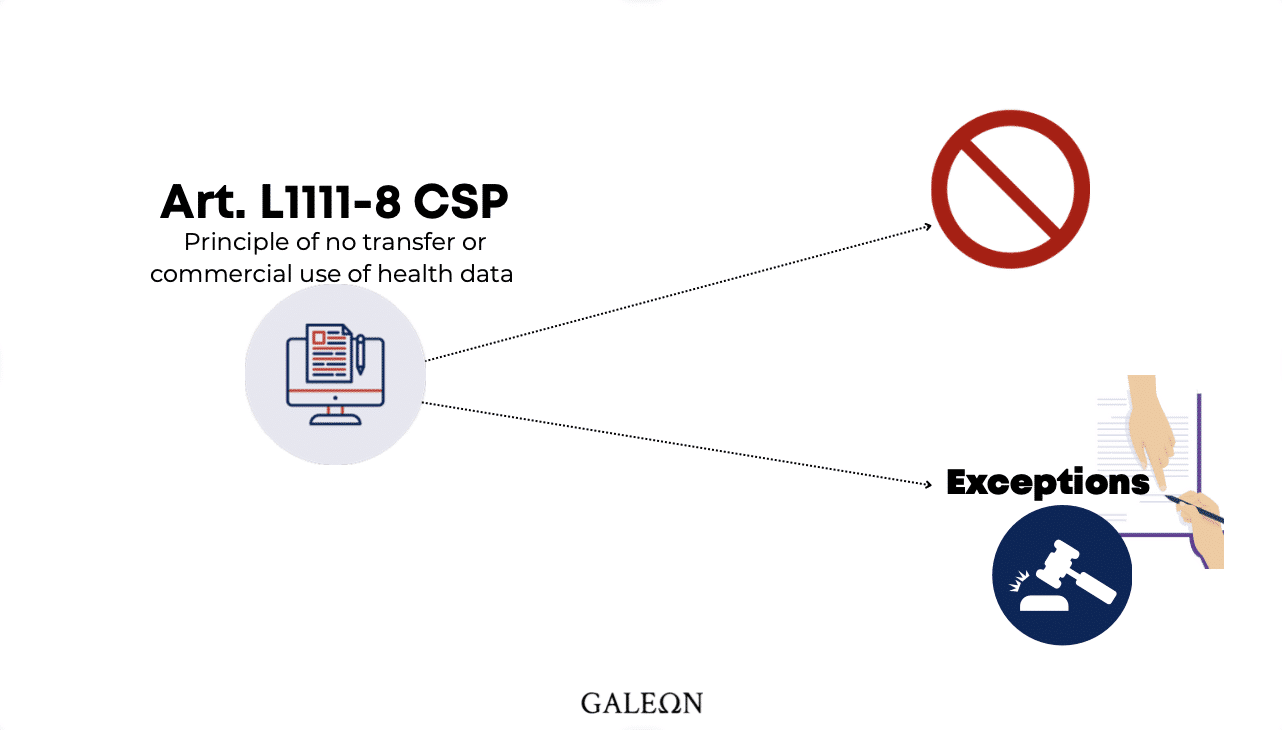
- Or article L.1111-8 of the CSP et seq. on the prohibition to transfer or commercially exploit health data.
What matters in the end is that we are aware of our rights regarding personal data.
Buy your first crypto easily with Galeon
PART 2 - Commercial exploitation of our data
Personal data can be divided into several categories of sensitive data and health data is one of them.
When it falls within the scope of article L.1111-8 of the CSP, it is protected by the principle of prohibition of transfer or commercial exploitation.
However, there are two exceptions:
- When the person gives his or her consent for the use of this health data. With this precision, that the consent must be given in a free, informed, univocal, and specially (? Be aware that the pre-checked boxes in a form are not considered as univocal).
- In some cases, consent is not required to use medical data for commercial purposes. For example, when it is a matter of public health prevention, preservation of the vital interests of the individual, or as a result of medical judgment...etc.
Again, each situation is considered on a case-by-case basis. ☝️
PART 3 - Health data in the US
The American system differs somewhat from the European system in terms of health data protection rules.
From a theoretical point of view, data protection is based more on the principle of the protection of individual liberties, whereas at the European level, it is based on the protection of the dignity of the person.
From a technical point of view, the regime is now characterized by a legal duality between federal and state laws. Moreover, there is no complete section reserved for personal data, but rather a differentiation by sector.
In the medical sector, we will have to comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996), and HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health of 2009).
Learn more about HIPAA and the HITECH Act.
A few words about HIPAA: the laws enacted set the legal framework for the use and disclosure of health data in the US. It is a federal law.
If the principle is that of non-disclosure of private data for health actors, exceptions exist.
The main thing to remember here is that depending on the territory in which a company wishes to export, it will have to comply with its rules. ☝️

PART 4 - Protecting health data in a decentralized world
The definition of health data, as it has been written, is designed to accommodate new cases.
On the other hand, the question that must necessarily be asked is that of the legal protection of this health data if it is to be stored in a decentralized environment.
Blockchain or DLT (Distributed ledger technology) type. As a reminder, a blockchain is a form of DLT, but not all DLTs are blockchains. ?
Thus, the main issue of this form of data structuring is without a doubt, their protection.
By writing health data on the blockchain or another form of ledger, we thus prevent the risks of exploitation and misuse of this data.
People can thus control the future of their personal data.
Moreover, this will allow them not to depend on an institution or an organization with little or no protection against possible attacks.
On the blockchain, the organization by blocks of data prevents the alteration of this information.
And, as we oftenly see, the loss of patient records has disastrous consequences, both for the health of individuals and for the operation of health institutions.
Would you like to be informed of Galeon's progress?
Subscribe to our newsletter!
